All Categories
Featured
2 people purchase joint annuities, which give a surefire revenue stream for the rest of their lives. When an annuitant dies, the interest made on the annuity is managed in different ways depending on the type of annuity. A type of annuity that quits all settlements upon the annuitant's death is a life-only annuity.

The initial principal(the amount at first deposited by the moms and dads )has actually currently been tired, so it's exempt to taxes once again upon inheritance. The incomes section of the annuity the interest or investment gains accrued over time is subject to earnings tax. Usually, non-qualified annuities do.
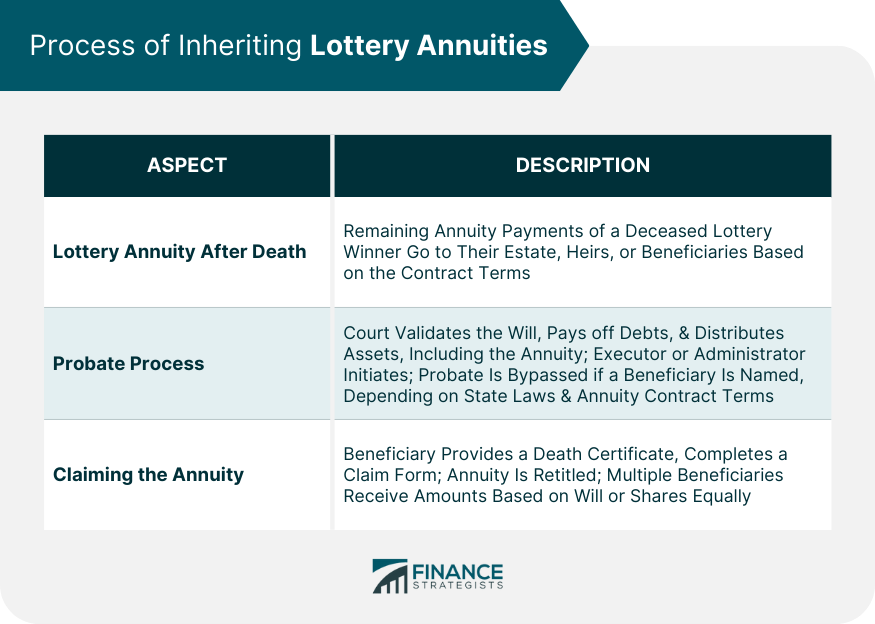
have actually passed away, the annuity's advantages typically revert to the annuity proprietor's estate. An annuity proprietor is not lawfully called for to inform current recipients about changes to beneficiary designations. The decision to transform beneficiaries is normally at the annuity owner's discernment and can be made without alerting the present beneficiaries. Given that an estate practically doesn't exist up until a person has died, this beneficiary designation would just enter effect upon the fatality of the named person. Commonly, when an annuity's owner dies, the marked recipient at the time of fatality is entitled to the benefits. The spouse can not change the recipient after the owner's fatality, also if the recipient is a minor. There may be particular stipulations for handling the funds for a small recipient. This frequently involves appointing a guardian or trustee to manage the funds till the child maturates. Usually, no, as the recipients are not liable for your debts. It is best to consult a tax expert for a particular solution related to your instance. You will certainly remain to receive payments according to the agreement timetable, however attempting to obtain a swelling sum or car loan is likely not an alternative. Yes, in almost all situations, annuities can be inherited. The exception is if an annuity is structured with a life-only payout alternative via annuitization. This sort of payout stops upon the fatality of the annuitant and does not give any residual value to successors. Yes, life insurance policy annuities are normally taxable
When withdrawn, the annuity's revenues are strained as normal revenue. The principal amount (the preliminary financial investment)is not taxed. If a beneficiary is not named for annuity advantages, the annuity continues normally go to the annuitant's estate. The distribution will certainly follow the probate process, which can postpone payments and may have tax effects. Yes, you can call a depend on as the beneficiary of an annuity.
How are beneficiaries taxed on Lifetime Annuities

This can offer better control over exactly how the annuity advantages are dispersed and can be part of an estate preparation approach to take care of and secure assets. Shawn Plummer, CRPC Retirement Planner and Insurance Representative Shawn Plummer is a certified Retired life Coordinator (CRPC), insurance coverage representative, and annuity broker with over 15 years of firsthand experience in annuities and insurance. Shawn is the creator of The Annuity Expert, an independent online insurance policy
firm servicing consumers throughout the USA. Via this platform, he and his team aim to remove the uncertainty in retirement preparation by assisting individuals discover the most effective insurance coverage at one of the most affordable rates. Scroll to Top. I understand all of that. What I do not understand is how in the past going into the 1099-R I was showing a reimbursement. After entering it, I currently owe tax obligations. It's a$10,070 distinction between the reimbursement I was anticipating and the taxes I currently owe. That appears really extreme. At a lot of, I would have anticipated the reimbursement to minimize- not entirely go away. An economic expert can help you determine exactly how best to take care of an inherited annuity. What takes place to an annuity after the annuity proprietor dies depends on the terms of the annuity agreement. Some annuities just quit dispersing revenue settlements when the owner dies. Oftentimes, however, the annuity has a survivor benefit. The recipient might obtain all the continuing to be cash in the annuity or an assured minimum payout, usually whichever is higher. If your moms and dad had an annuity, their agreement will certainly define that the recipient is and may
right into a retired life account. An inherited individual retirement account is an unique pension utilized to distribute the properties of a departed person to their recipients. The account is signed up in the deceased person's name, and as a beneficiary, you are not able to make added payments or roll the acquired individual retirement account over to another account. Only certified annuities can be rolledover right into an acquired individual retirement account.
Latest Posts
Decoding Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Everything You Need to Know About Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity What Is the Best Retirement Option? Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Retirement
Understanding Financial Strategies Everything You Need to Know About Financial Strategies Defining What Is A Variable Annuity Vs A Fixed Annuity Advantages and Disadvantages of Choosing Between Fixed
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments A Comprehensive Guide to Fixed Vs Variable Annuity What Is Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity? Advantages and Disadvantages of Indexed Annuity
More
Latest Posts